Test Performance
Test Performance
This section will test the performance of STG326 - SAZ.
There are many disk performance tools out there. We have pre-installed DiskSpd and fio on the Windows Instance 0 instance. If you are familiar with another tool and would prefer using it to test performance, feel free to download and use it.
$client = new-object System.Net.WebClient
$client.DownloadFile("https://lab.com/microsoft/diskspd/releases/download/v2.0.21a/DiskSpd.zip","C:\Tools\DiskSpd-2.0.21a\DiskSpd-2.0.21a.zip")
Expand-Archive -LiteralPath C:\Tools\DiskSpd-2.0.21a\DiskSpd-2.0.21a.zip -DestinationPath C:\Tools\DiskSpd-2.0.21a
Note
It will take approximately 30 minutes to complete this section.
Important
Read through all steps below and watch the quick video before continuing.
DiskSpd Read tests
-
Access the remote desktop session to Windows Instance 0.
-
Click Start >> Windows PowerShell.
Important
This section assumes that STG326 - SAZ is mapped as the Z:/ drive. If your Windows Instance 0 does not have a mapped Z:/ drive, map STG326 - SAZ as the Z:/ drive (see the previous section for step-by-step instructions).
-
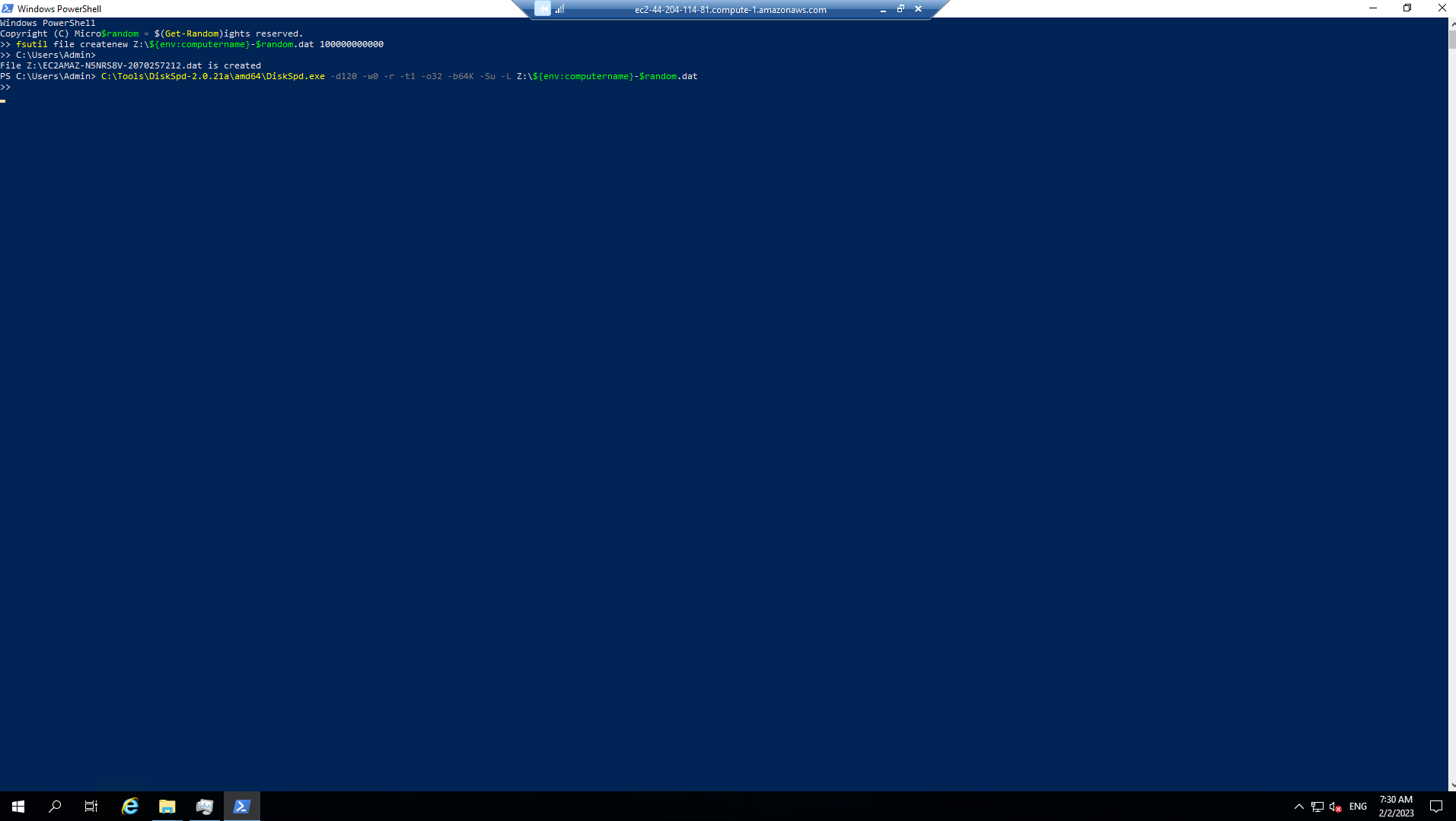
Run the script below in the PowerShell seccion to create a 100 GB sparse file.
$random = $(Get-Random)
fsutil file createnew Z:\${env:computername}-$random.dat 100000000000
- Runthe DiskSpeed script below to test read performance of the mapped Z: drive
C:\Tools\DiskSpd-2.0.21a\amd64\DiskSpd.exe -d120 -w0 -r -t1 -o32 -b64K -Su -L Z:\${env:computername}-$random.dat
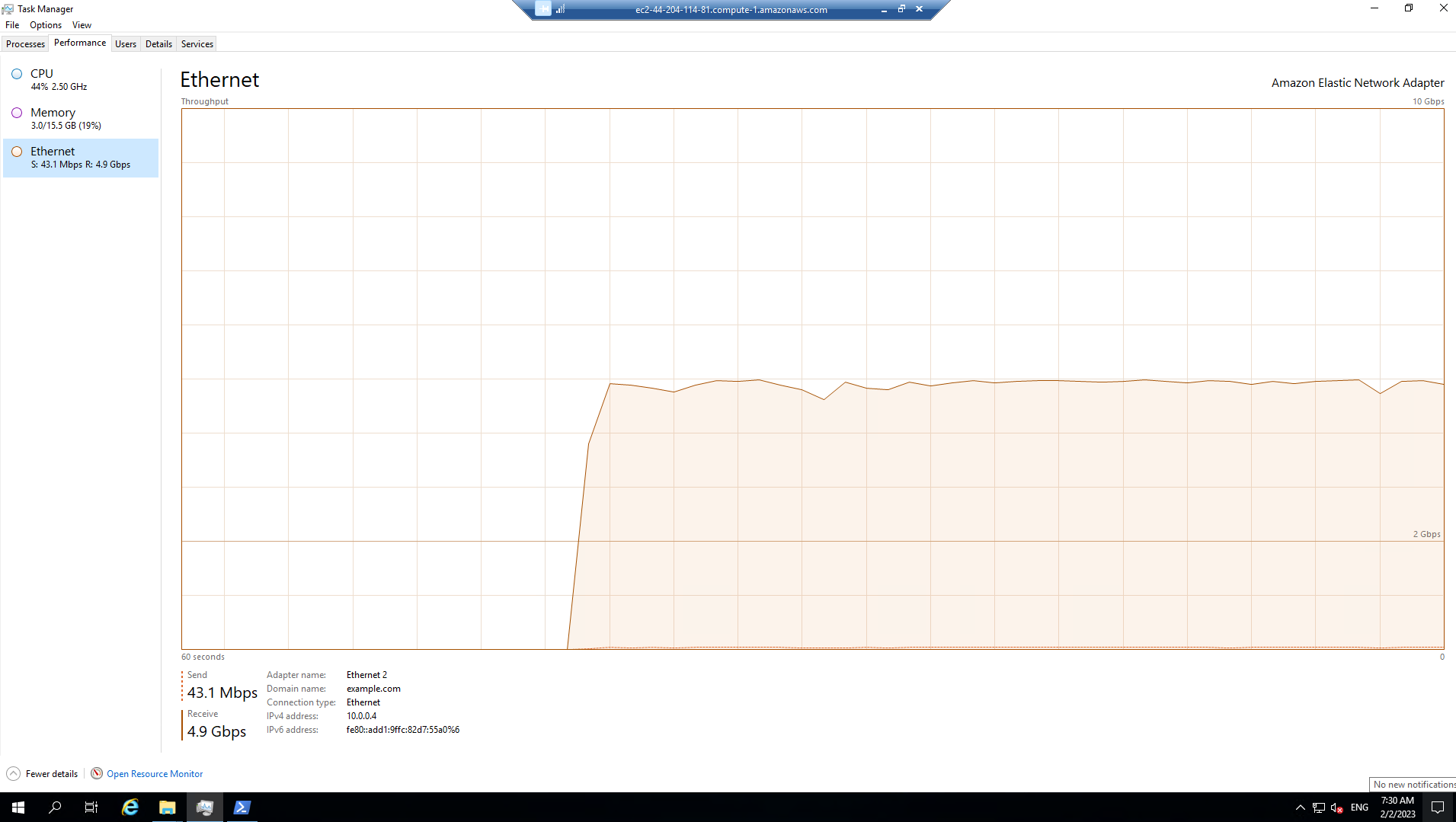
While the script is running, open Task Manager and monitor network performance (e.g. Start >> Task Manager >> More details>> Performance (tab) >> Ethernet).
-
What is the baseline throughput of the file system? - This was configured when the file system was created and is available from the Amazon FSx console.
-
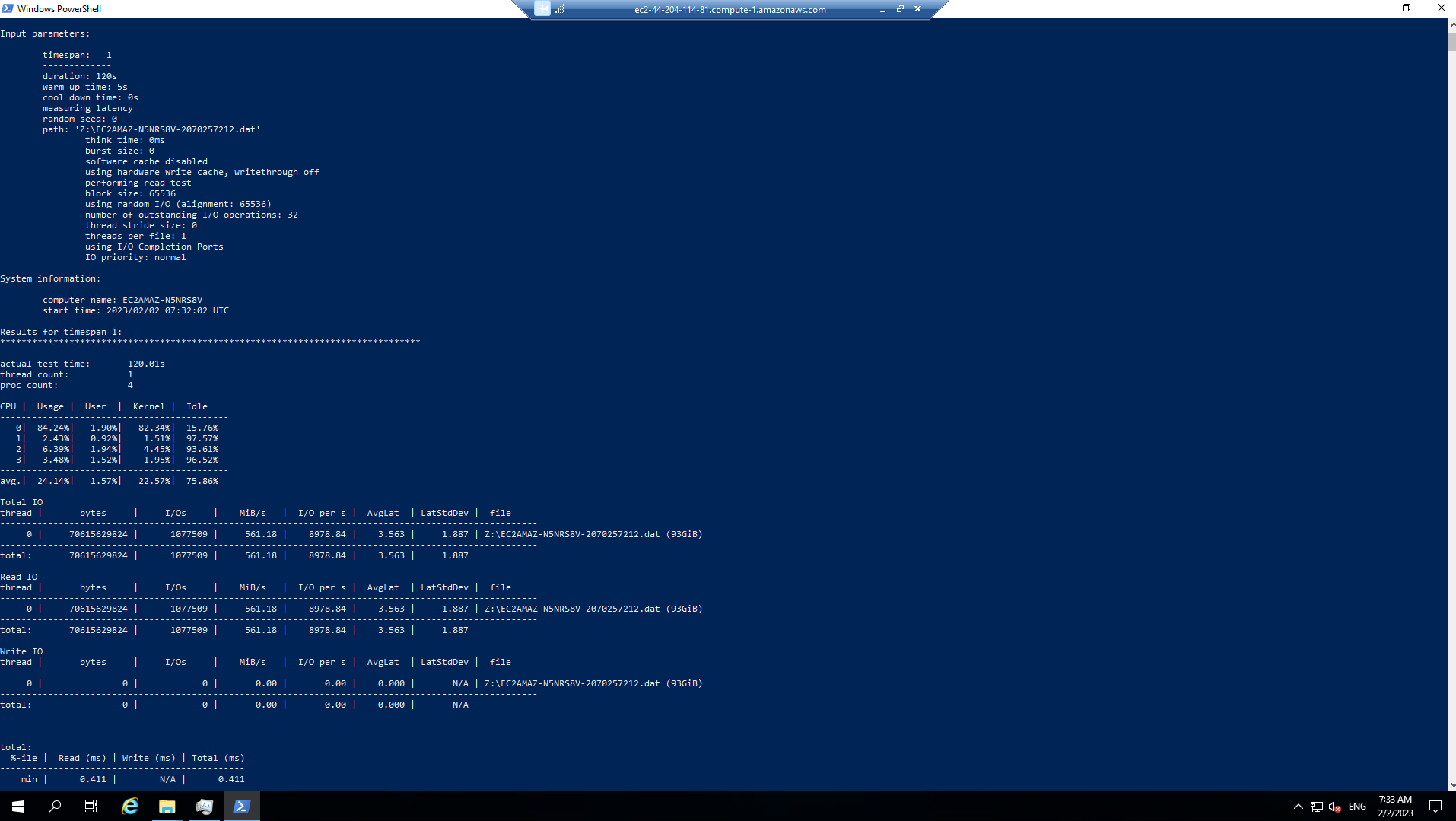
What was the peak read throughput you achieved?
-
What was the P99 (99th %-tile) of your test?
-
What was the Total Read IO MiB/s?
-
What was the I/O per second?
-
What was the AvgLat?
-
Why is your current throughput greater than the baseline throughput?
-
-
Experiment with different DiskSpd parameter settings. Use the table below as a guide. Test with different block sizes (-b), number of outstanding I/O requests (-o), number of threads per file (-t), and enable/disable software caching (-Su).
Parameter Description -b<size>[K|M|G]Block size in bytes or KiB, MiB, or GiB (default = 64K). -o<count>Number of outstanding I/O requests per-target per-thread. (1 = synchronous I/O, unless more than one thread is specified with by using -F.) (default = 2) -r<size>[K|M|G]Random I/O aligned to the specified number of bytes or KiB, MiB, GiB, or blocks. Overrides -s (default stride = block size). -s<size>[K|M|G]Sequential stride size, offset between subsequent I/O operations in bytes or KiB, MiB, GiB, or blocks. Ignored if -r is specified (default access = sequential, default stride = block size). -t<count>Number of threads per target. Conflicts with -F, which specifies the total number of threads. -SuDisable software caching. -
What different parameters did you test?
-
How did the different parameter options alter the results?
-
DiskSpd Write tests
-
From the remote desktop session to Windows Instance 0, open a PowerShell window.
Important
This section assumes that STG326 - SAZ is mapped as the Z:/ drive. If your Windows Instance 0 does not have a mapped Z:/ drive, map STG326 - SAZ as the Z:/ drive (see the previous section for step-by-step instructions).
-
Run the DiskSpeed script below to test write performance of the mapped Z: drive
$random = $(Get-Random)
C:\Tools\DiskSpd-2.0.21a\amd64\DiskSpd.exe -d120 -c2G -s64K -w100 -t1 -o32 -b64K -Sh -L Z:\${env:computername}-$random.dat
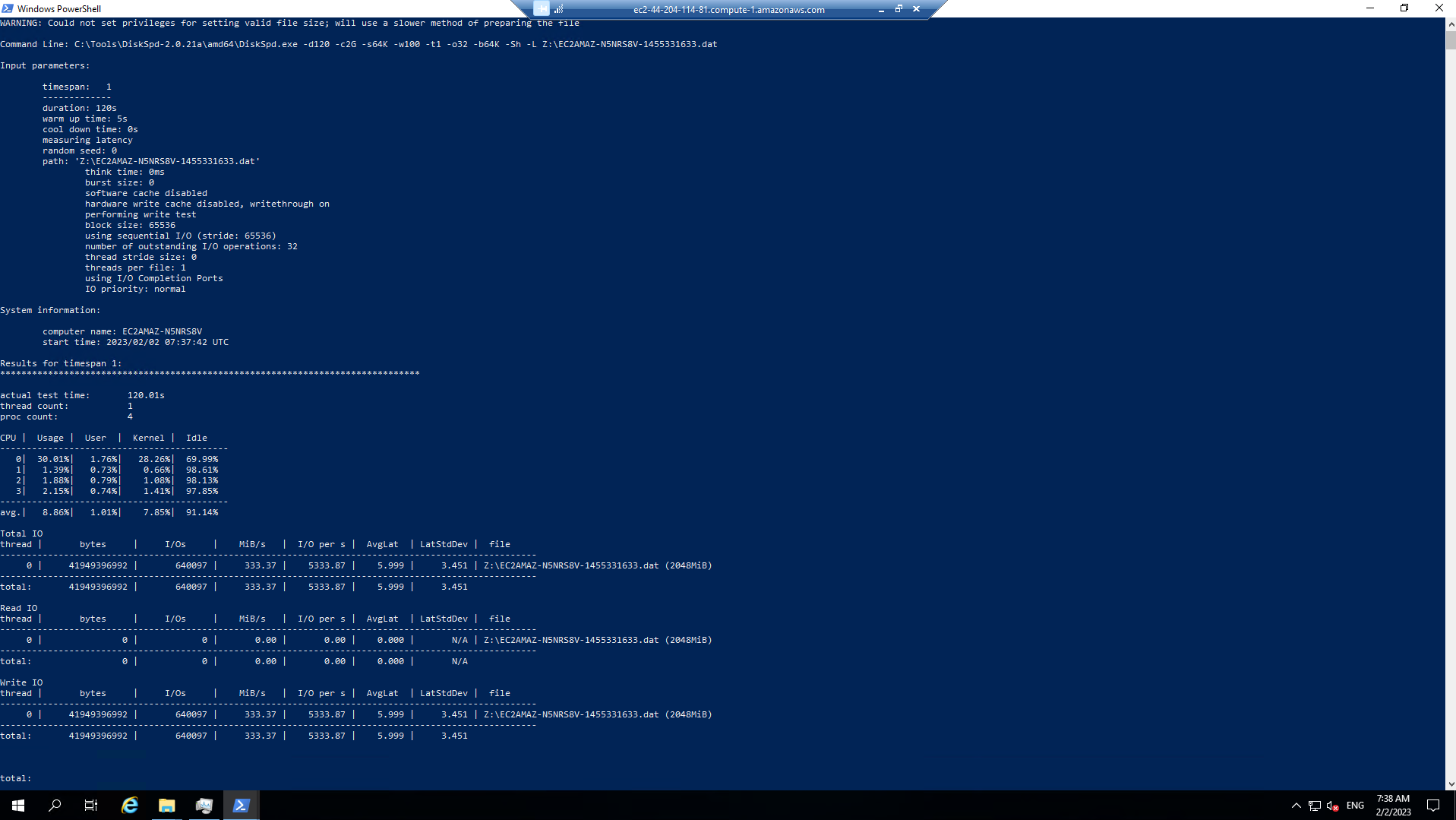
While the script is running, open Task Manager and monitor network performance (e.g. Start >> Task Manager >> Performance (tab) >> Ethernet).
-
What is the baseline throughput of the file system? - This was configured when the file system was created and is available from the Amazon FSx console.
-
What was the peak write throughput you achieved?
-
What was the P99 (99th %-tile) of your test?
-
What was the Total Write IO MiB/s?
-
What was the I/O per second?
-
What was the AvgLat?
-
Why is your current throughput greater than the baseline throughput?
-
-
Experiment with different DiskSpd parameter settings. Use the table below as a guide. Test with different file sizes (-c), different block sizes (-b), number of outstanding I/O requests (-o), number of threads per file (-t), random I/O (-r) or sequential I/O (-s), and enable/disable software & hardware write caching (-Sh).
Parameter Description -d<seconds>Duration in seconds. -b<size>[K|M|G]Block size in bytes or KiB, MiB, or GiB (default = 64K). -c<size>[K|M|G]Create files of the specified size. Size can be stated in bytes or KiBs, MiBs, GiBs, or blocks. -r<size>[K|M|G]Random I/O aligned to the specified number of bytes or KiB, MiB, GiB, or blocks. Overrides -s. -s<size>[K|M|G]Sequential stride size, offset between subsequent I/O operations in bytes or KiB, MiB, GiB, or blocks. Ignored if -r is specified (default access = sequential, default stride = block size). -o<count>Number of outstanding I/O requests per-target per-thread. (1 = synchronous I/O, unless more than one thread is specified with by using -F.) (default = 2) -t<count>Number of threads per target. Conflicts with -F, which specifies the total number of threads. -ShDisables both software caching and hardware write caching. -
What different parameters did you test?
-
How did the different parameter options alter the results?
-
fio read tests
-
From the remote desktop session to Windows Instance 0, open a PowerShell window.
Important
This section assumes that STG326 - SAZ is mapped as the Z:/ drive. If your Windows Instance 0 does not have a mapped Z:/ drive, map STG326 - SAZ as the Z:/ drive (see the previous section for step-by-step instructions).
-
Run the fio script below to test read performance of the mapped Z: drive
$random = $(Get-Random)
C:\Tools\fio-3.16-x64\fio --randrepeat=1 --direct=1 --name="Z:\${env:computername}-$random.dat" --numjobs=1 --bs=64K --iodepth=32 --size=1024M --readwrite=read --rwmixread=100 --thread --time_based --runtime=120
While the script is running, open Task Manager and monitor network performance (e.g. Start >> Task Manager >> Performance (tab) >> Ethernet).
- What was the peak read throughput?
- What was the average read throughput?
- What was the average IOPS?
- How many GB did you read in 120 seconds?
- Experiment with different fio parameter settings. Use the table below as a guide. Test with direct I/O enabled or disabled (–direct), different block sizes (–bs), number of outstanding I/O requests (–iodepth), number of jobs (–numjobs), random read, random write, sequential read, sequential write (–readwrite), and mixture of reads and writes (–rwmixread).
| Parameter | Description |
--direct=[0|1] |
Use buffered (0) or non-buffered (1) I/O. |
--bs=<size>[K|M|G] |
Block size in bytes or KiB, MiB, or GiB (default = 64K). |
--numjobs=<count> |
Number of clones (processes/threads performing the same workload) of this job. Default: 1. |
--readwrite=[read|write|randread|randwrite] |
Type of I/O pattern (read = sequential read; write = sequential write; randread = random read; randwrite = random write). |
--iodepth=<count> |
Number of I/O units to keep in flight against the file. |
--rwmixread=<percent> |
Percentage of a mixed workload that should be reads. The outstanding percentage will be writes. |
-
What different parameters did you test?
-
How did the different parameter options alter the results?
fio write tests
-
From the remote desktop session to Windows Instance 0, open a PowerShell window.
Important
This section assumes that STG326 - SAZ is mapped as the Z:/ drive. If your Windows Instance 0 does not have a mapped Z:/ drive, map STG326 - SAZ as the Z:/ drive (see the previous section for step-by-step instructions).
-
Run the fio script below to test write performance of the mapped Z: drive
$random = $(Get-Random)
C:\Tools\fio-3.16-x64\fio --randrepeat=1 --direct=1 --name="Z:\${env:computername}-$random.dat" --numjobs=1 --bs=64K --iodepth=32 --size=1024M --readwrite=write --rwmixwrite=100 --thread --time_based --runtime=120
While the script is running, open Task Manager and monitor network performance (e.g. Start >> Task Manager >> Performance (tab) >> Ethernet).
- What was the peak write throughput?
- What was the average write throughput?
- What was the average IOPS?
- How many GB did you write in 120 seconds?
- Experiment with different fio parameter settings. Use the table below as a guide. Test with direct I/O enabled or disabled (–direct), different block sizes (–bs), number of outstanding I/O requests (–iodepth), number of jobs (–numjobs), random read, random write, sequential read, sequential write (–readwrite), and mixture of reads and writes (–rwmixwrite).
| Parameter | Description |
--direct=[0|1] |
Use buffered (0) or non-buffered (1) I/O. |
--bs=<size>[K|M|G] |
Block size in bytes or KiB, MiB, or GiB (default = 64K). |
--numjobs=<count> |
Number of clones (processes/threads performing the same workload) of this job. Default: 1. |
--readwrite=[read|write|randread|randwrite] |
Type of I/O pattern (read = sequential read; write = sequential write; randread = random read; randwrite = random write). |
--iodepth=<count> |
Number of I/O units to keep in flight against the file. |
--rwmixwrite=<percent> |
Percentage of a mixed workload that should be writes. The outstanding percentage will be reads |
-
What different parameters did you test?
-
How did the different parameter options alter the results?
-
Close all the PowerShell windows. Run exit.
-
Close the File Explorer window.
-
Close the Task Manager window.
-